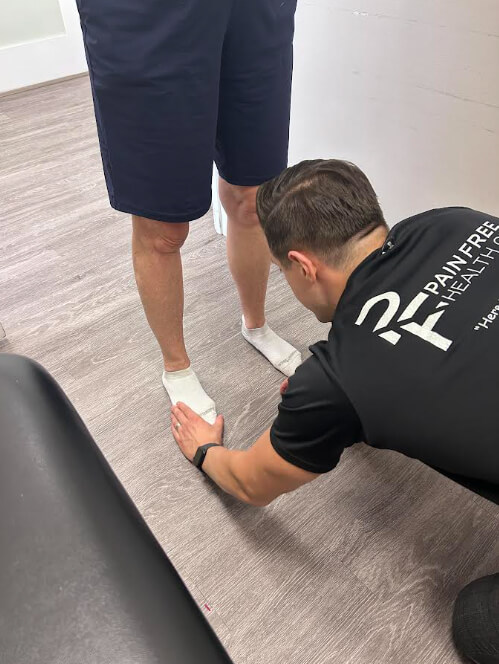
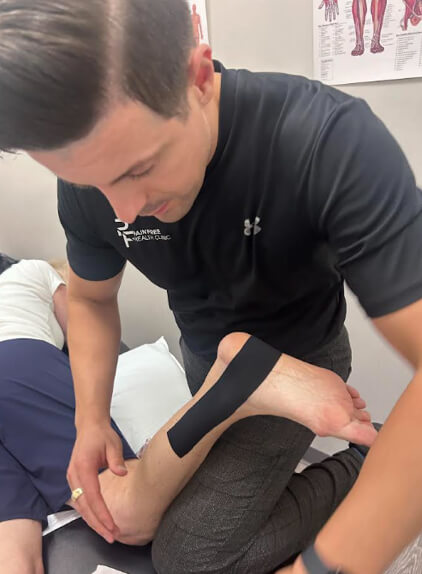
Posterior shin splints are a common yet often misunderstood lower leg injury. They cause pain along the inside of the shin, typically due to inflammation of the posterior tibialis muscle and tendon. If untreated, shin splints can progress into stress reactions or stress fractures, leading to long recovery times.
At Pain Free Health, we regularly treat athletes, runners, and active individuals with shin pain. This case study shows how a full assessment and targeted treatment can prevent a mild injury from turning into a more serious problem.
Our patient came in with:
The posterior tibialis muscle plays a key role in supporting the arch of the foot. Overuse, poor biomechanics, or inadequate footwear can cause it to work harder than it should, leading to:
Common risk factors include:
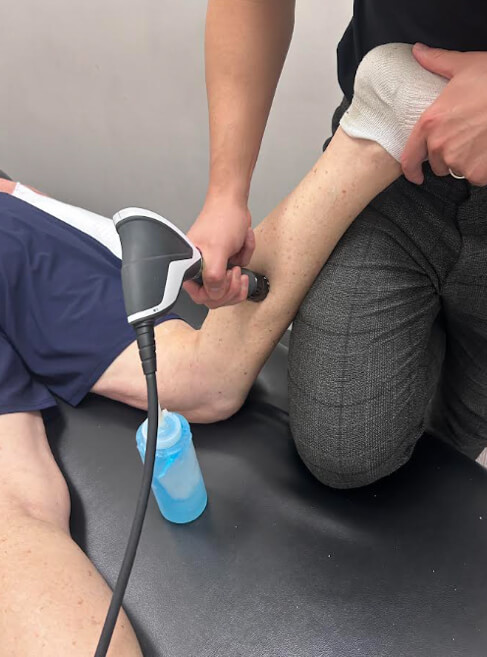
1. Reduce Pain & Inflammation
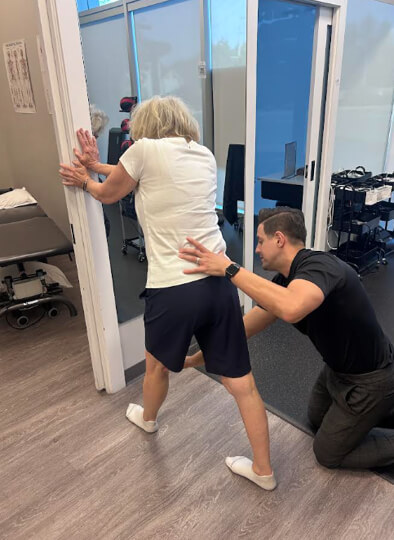
2. Correct Biomechanics
3. Strengthen Key Muscles
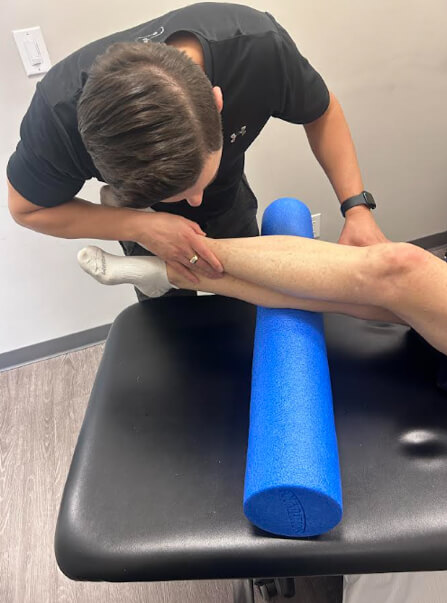
4. Mobility & Self-Care
With consistent treatment and home exercises, most mild-to-moderate posterior shin splints improve in 4–6 weeks. More severe cases or stress fractures may require 8–12 weeks and modified activity.
Ignoring shin pain can lead to:
Early physiotherapy assessment can stop the injury from progressing, speed up healing, and improve long-term lower limb health.
Pain Free Health offers posterior shin splint assessment, treatment, and rehabilitation at multiple locations:
If you’re struggling with shin splints, stress fractures, or lower leg pain, book an appointment today and get back to moving pain-free.